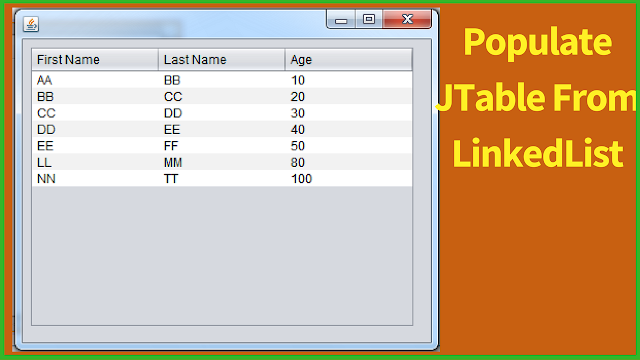
Java - How To Display Data From A LinkedList In Java
2: how to dispaly data from it
3: how to add an elements in the first
4: how to add an elements in the end
5: how to clear all elements from it
and more........
Source Code:
package javaapp;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class Woirk {
public static void main(String[] args){
LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<Integer>();
LinkedList<Integer> list2 = new LinkedList<Integer>();
LinkedList<Integer> list3 = new LinkedList<Integer>();
//add element to the end of the list
list.add(6);
list.add(2);
list.add(8);
list.add(5);
list.add(7);
list.add(8);
list.add(16);
list.add(12);
list.add(8);
list.add(15);
list.add(17);
list.add(8);
System.out.println(list);
//add element to list2
list2.add(100);
list2.add(1000);
list2.add(10000);
//add element to list3
list3.add(11111);
list3.add(33333);
list3.add(44444);
//add element at the specified position in the list
list.add(1,10);
System.out.println(list);
//add collection to the and of another collection
list.addAll(list2);
System.out.println(list);
//add collection to another collection in the specified position
list.addAll(4, list3);
System.out.println(list);
//add element in the beginning of the list
list.addFirst(0);
System.out.println(list);
//add element in the end of the list
list.addLast(999999);
System.out.println(list);
//clone the list
LinkedList<Integer> listClone = new LinkedList<Integer>();
listClone = (LinkedList<Integer>) list.clone();
System.out.println(listClone);
//check if the given element exist in the list
boolean exist = list.contains(8);
System.out.println(exist);
//5 way to get the first element of the linkedlist
System.out.println(list.element());
System.out.println(list.getFirst());
System.out.println(list.get(0));
System.out.println(list.peek());
System.out.println(list.peekFirst());
//3 way to get the last element of the linkedlist
System.out.println(list.getLast());
System.out.println(list.get(list.size()-1));
System.out.println(list.peekLast());
//return the index of the element
int index = list.indexOf(8);
System.out.println(index);
//return the last index of the element
int lastIndex = list.lastIndexOf(8);
System.out.println(lastIndex);
//insert element at the beginning of the list
list.offerFirst(2015);
//insert element at the end of the list
list.offerLast(500000);
System.out.println(list);
//5 way to remove the first element in the list
list.poll();
list.pollFirst();
list.remove();
list.removeFirst();
list.remove(0);
System.out.println(list);
//3 way to remove the first element in the list
list.pollLast();
list.removeLast();
list.remove(list.size()-1);
System.out.println(list);
//delete the first element of a list who is equal to the given element
list.removeFirstOccurrence(8);
System.out.println(list);
// you can also use
//list.remove(8);
//delete the last element of a list who is equal to the given element
list.removeLastOccurrence(8);
System.out.println(list);
//replace element in the given index with the given element
list.set(0, 123456789);
System.out.println(list);
//how to use toArray() methode
Object[] obj = list.toArray();
for(Object o : obj)
System.out.print(o+" - ");
System.out.println();
//how to use toArray(T[] a) methode
Integer[] t = list.toArray(new Integer[0]);
for(Integer i : t)
System.out.print(i+" - ");
System.out.println();
System.out.println("List Size Before The Clear: "+list.size());
//clear all elements in the list
list.clear();
System.out.println("List Size After The Clear: "+list.size());
}
}
//OUTPUT:
[6, 2, 8, 5, 7, 8, 16, 12, 8, 15, 17, 8]
[6, 10, 2, 8, 5, 7, 8, 16, 12, 8, 15, 17, 8]
[6, 10, 2, 8, 5, 7, 8, 16, 12, 8, 15, 17, 8, 100, 1000, 10000]
[6, 10, 2, 8, 11111, 33333, 44444, 5, 7, 8, 16, 12, 8, 15, 17, 8, 100, 1000, 10000]
[0, 6, 10, 2, 8, 11111, 33333, 44444, 5, 7, 8, 16, 12, 8, 15, 17, 8, 100, 1000, 10000]
[0, 6, 10, 2, 8, 11111, 33333, 44444, 5, 7, 8, 16, 12, 8, 15, 17, 8, 100, 1000, 10000, 999999]
[0, 6, 10, 2, 8, 11111, 33333, 44444, 5, 7, 8, 16, 12, 8, 15, 17, 8, 100, 1000, 10000, 999999]
true
0
0
0
0
0
999999
999999
999999
4
16
[2015, 0, 6, 10, 2, 8, 11111, 33333, 44444, 5, 7, 8, 16, 12, 8, 15, 17, 8, 100, 1000, 10000, 999999, 500000]
[8, 11111, 33333, 44444, 5, 7, 8, 16, 12, 8, 15, 17, 8, 100, 1000, 10000, 999999, 500000]
[8, 11111, 33333, 44444, 5, 7, 8, 16, 12, 8, 15, 17, 8, 100, 1000]
[11111, 33333, 44444, 5, 7, 8, 16, 12, 8, 15, 17, 8, 100, 1000]
[11111, 33333, 44444, 5, 7, 8, 16, 12, 8, 15, 17, 100, 1000]
[123456789, 33333, 44444, 5, 7, 8, 16, 12, 8, 15, 17, 100, 1000]
123456789 - 33333 - 44444 - 5 - 7 - 8 - 16 - 12 - 8 - 15 - 17 - 100 - 1000 -
123456789 - 33333 - 44444 - 5 - 7 - 8 - 16 - 12 - 8 - 15 - 17 - 100 - 1000 -
List Size Before The Clear: 13
List Size After The Clear: 0