How to Create a Pie Chart In Python Tkinter
In this Python tutorial we will create a pie chart using the Tkinter library for the graphical user interface.
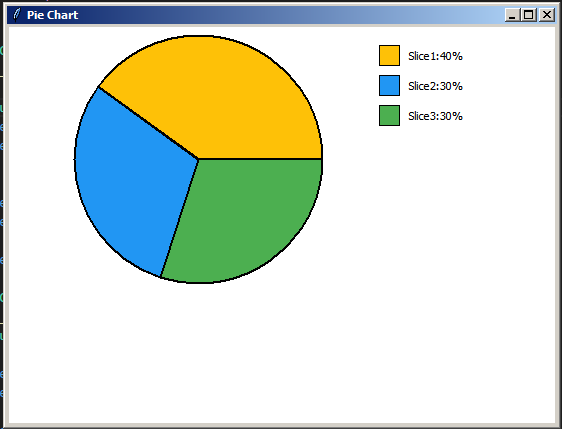
The pie chart displays three slices with predefined colors and values, along with a legend indicating the percentage of each slice.
What We Are Gonna Use In This Project:
- Python Programming Language.- Tkinter for GUI.
- VS Code Editor.
- VS Code Editor.
Project Source Code:
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import Canvas
class PieChart(tk.Tk):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.title("Pie Chart")
self.geometry("550x400")
# Create the PieChartPanel instance and pack it into the root window
self.pie_chart_panel = PieChartPanel(self)
self.pie_chart_panel.pack(fill=tk.BOTH, expand=True)
self.mainloop()
class PieChartPanel(Canvas):
def __init__(self, master = None):
super().__init__(master, bg="white")
# Define slice colors and data values for the pie chart
self.slice_colors = ["#FEC107", "#2196F3", "#4CAF50"]
self.data = [40, 30, 30]
# Draw the pie chart
self.draw_pie_chart()
def draw_pie_chart(self):
# Get the width and height of the canvas
width = self.winfo_reqwidth()
height = self.winfo_reqheight()
# Calculate the diameter of the pie chart
diameter = min(width, height) - 20
# Calculate the starting position of the pie chart
x = (width - diameter) / 2
y = (height - diameter) / 2
start_angle = 0
# Draw each slice of the pie chart
for i, value in enumerate(self.data):
# Calculate the angle of the current slice
arc_angle = int(value / 100 * 360)
# Draw the arc representing the slice
self.create_arc(x, y, x + diameter, y + diameter, start = start_angle,
extent=arc_angle, fill=self.slice_colors[i], outline="black", width=2)
# Update the start angle for the next slice
start_angle += arc_angle
# Draw the legend for the pie chart
legend_x = width - 110
legend_y = 20
for i, value in enumerate(self.data):
# Draw colored rectangles representing each slice
self.create_rectangle(legend_x + 100, legend_y, legend_x + 120,
legend_y + 20, fill=self.slice_colors[i])
# Add text indicating the percentage of each slice
self.create_text(legend_x + 130, legend_y + 10,
text = f"Slice{i + 1}:{value}%", anchor=tk.W)
legend_y += 30
if __name__ == "__main__":
PieChart()