How to Create an Image Editor Project in Python Using Tkinter
In this Python tutorial, we will see how to create a simple photo editor application using Tkinter for the GUI and the Pillow library for image manipulation.
This photo editor application allows users to open an image and apply various editing effects such as blur, grayscale, brightness enhancement, rotation, color inversion, edge detection, and mirroring.
Users can also crop the image interactively.
What We Are Gonna Use In This Project:
- Python Programming Language.- Tkinter for GUI.
- VS Code Editor.
- VS Code Editor.
Project Source Code:
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import filedialog, simpledialog
# pip install Pillow
from PIL import Image, ImageTk, ImageFilter, ImageEnhance, ImageOps, ImageChops
class PhotoEditorApp:
def __init__(self, root):
self.root = root
self.root.title("Photo Editor")
self.root.geometry("750x450")
self.canvas = tk.Canvas(self.root, bg="white")
self.canvas.pack(fill=tk.BOTH, expand=True)
# Create menu bar
self.menubar = tk.Menu(self.root)
self.root.config(menu = self.menubar)
# Create File menu with Open and Exit options
self.file_menu = tk.Menu(self.menubar, tearoff=0)
self.menubar.add_cascade(label="File", menu = self.file_menu)
self.file_menu.add_command(label = "Open", command = self.open_image)
self.file_menu.add_separator()
self.file_menu.add_command(label = "Exit", command = self.root.quit)
# Create Edit menu with various image manipulation options
self.edit_manu = tk.Menu(self.menubar, tearoff = 0)
self.menubar.add_cascade(label = "Edit", menu=self.edit_manu)
self.edit_manu.add_command(label = "Blur", command = self.apply_blur)
self.edit_manu.add_command(label = "Grayscale", command = self.apply_grayscale)
self.edit_manu.add_command(label = "Enhance Brightness",
command = self.enhance_brightness)
self.edit_manu.add_command(label = "Rotate", command = self.rotate_image)
self.edit_manu.add_command(label = "Crop", command = self.crop_image)
self.edit_manu.add_command(label = "Invert Colors",
command = self.inver_colors)
self.edit_manu.add_command(label = "Edge Detection",
command = self.edge_detection)
self.edit_manu.add_command(label = "Mirror", command = self.mirror_image)
self.edit_manu.add_command(label = "Original State",
command = self.display_original_state)
# Variables for cropping
self.crop_start_x = None
self.crop_start_y = None
self.crop_rect = None
# Bind events for cropping
self.canvas.bind("<Button-1>", self.start_crop)
self.canvas.bind("<B1-Motion>", self.update_crop)
self.canvas.bind("<ButtonRelease-1>", self.crop_image)
def open_image(self):
# Open a file dialog to select an image file
file_path = filedialog.askopenfilename(filetypes = [("Image Files" ,
"*.png *.jpg *.jpeg *.bmp *.gif")])
if file_path:
# Open the selected image file using PIL
self.image = Image.open(file_path)
# Save a copy of the original image
self.original_image = self.image.copy()
self.image_tk = ImageTk.PhotoImage(self.image)
# Display the image on the canvas
self.canvas.create_image(0,0, anchor = tk.NW, image=self.image_tk)
def apply_blur(self):
# Apply a blur filter to the image
if self.image:
blurred_image = self.image.filter(ImageFilter.BLUR)
self.display_image(blurred_image)
def apply_grayscale(self):
# Convert the image to grayscale
if self.image:
grayscale_image = self.image.convert("L")
self.display_image(grayscale_image)
def enhance_brightness(self):
# Enhance the brightness of the image
if self.image:
enhancer = ImageEnhance.Brightness(self.image)
enhanced_image = enhancer.enhance(1.5)
self.display_image(enhanced_image)
def rotate_image(self):
# Rotate the image based on user input
if self.image:
degrees = simpledialog.askinteger("Rotate Image",
"Enter rotation angle(degrees):", parent = self.root)
if degrees:
rotated_image = self.image.rotate(degrees, expand=True)
self.display_image(rotated_image)
def inver_colors(self):
# Invert the colors of the image
if self.image:
inverted_image = ImageOps.invert(self.image)
self.display_image(inverted_image)
def edge_detection(self):
# Apply edge detection filter to the image
if self.image:
edge_detection = self.image.filter(ImageFilter.FIND_EDGES)
self.display_image(edge_detection)
def mirror_image(self):
# Mirror the image horizontally
if self.image:
mirrored_image = ImageOps.mirror(self.image)
self.display_image(mirrored_image)
def start_crop(self, event):
# Record the starting position of the crop
self.crop_start_x = self.canvas.canvasx(event.x)
self.crop_start_y = self.canvas.canvasy(event.y)
def update_crop(self, event):
"""
Update the crop rectangle during mouse motion.
Args:
event: Mouse event containing information about the current mouse position.
"""
# Get current mouse position relative to the canvas
cur_x = self.canvas.canvasx(event.x)
cur_y = self.canvas.canvasy(event.y)
# Delete previous crop rectangle if it exists
if self.crop_rect:
self.canvas.delete(self.crop_rect)
# Create a new crop rectangle based on the starting position
# and current position
self.crop_rect = self.canvas.create_rectangle(self.crop_start_x,
self.crop_start_y, cur_x, cur_y, outline="red")
def crop_image(self, event=None):
"""
Crop the image based on the crop rectangle.
Args:
event: Mouse event triggering the crop action (optional).
"""
if self.crop_rect:
# Get current mouse position relative to the canvas
if event:
cur_x = self.canvas.canvasx(event.x)
cur_y = self.canvas.canvasy(event.y)
# Determine the coordinates of the crop rectangle
x1, y1 = min(self.crop_start_x, cur_x), min(self.crop_start_y, cur_y)
x2, y2 = max(self.crop_start_x, cur_x), max(self.crop_start_y, cur_y)
# Crop the image using the determined coordinates
cropped_image = self.image.crop((x1, y1, x2, y2))
self.display_image(cropped_image)
# Delete the crop rectangle
self.canvas.delete(self.crop_rect)
self.crop_rect = None
def display_original_state(self):
# Display the image in its original state
if self.image:
self.display_image(self.original_image)
def display_image(self, img):
# Display the given image on the canvas
self.image = img
self.image_tk = ImageTk.PhotoImage(self.image)
self.canvas.create_image(0, 0, anchor = tk.NW, image = self.image_tk)
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = tk.Tk()
app = PhotoEditorApp(root)
root.mainloop()
The Final Result:
 |
| Edge Detection |
 |
| GrayScale |
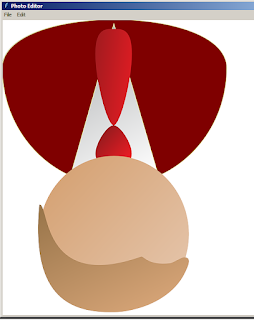 |
| rotate (180 degree) |
 |
| brightness enhancement |
 |
| grayscale |
 |
| blur |
 |
| invert colors |
 |
| edge detection |
 |
| crop image |
 |
| mirror |








